This block generates an output signal y[:] by constant, linear or cubic Hermite spline interpolation in a table. The time points and function values are stored in a matrix table[i,j], where the first column table[:,1] contains the time points and the other columns contain the data to be interpolated.
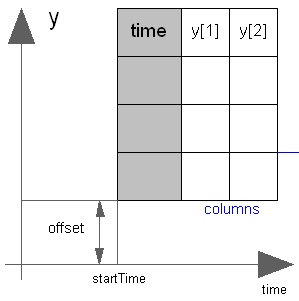
Via parameter columns it can be defined which columns of the table are interpolated. If, e.g., columns={2,4}, it is assumed that 2 output signals are present and that the first output is computed by interpolation of column 2 and the second output is computed by interpolation of column 4 of the table matrix. The table interpolation has the following properties:
smoothness = 1: Linear interpolation
= 2: Akima interpolation: Smooth interpolation by cubic Hermite
splines such that der(y) is continuous, also if extrapolated.
= 3: Constant segments
= 4: Fritsch-Butland interpolation: Smooth interpolation by cubic
Hermite splines such that y preserves the monotonicity and
der(y) is continuous, also if extrapolated.
= 5: Steffen interpolation: Smooth interpolation by cubic Hermite
splines such that y preserves the monotonicity and der(y)
is continuous, also if extrapolated.
= 6: Modified Akima interpolation: Smooth interpolation by cubic
Hermite splines such that der(y) is continuous, also if
extrapolated. Additionally, overshoots and edge cases of the
original Akima interpolation method are avoided.
extrapolation = 1: Hold the first or last value of the table,
if outside of the table scope.
= 2: Extrapolate by using the derivative at the first/last table
points if outside of the table scope.
(If smoothness is LinearSegments or ConstantSegments
this means to extrapolate linearly through the first/last
two table points.).
= 3: Periodically repeat the table data (periodical function).
= 4: No extrapolation, i.e. extrapolation triggers an error
timeEvents = 1: Always generate time events at interval boundaries
= 2: Generate time events at discontinuities (defined by duplicated sample points)
= 3: No time events at interval boundaries
For interpolation by constant segments time events are always
generated at interval boundaries. For smooth interpolation by cubic
Hermite splines no time events are generated at interval
boundaries.Example:
table = [0, 0;
1, 0;
1, 1;
2, 4;
3, 9;
4, 16];
extrapolation = 2 (default), timeEvents = 2
If, e.g., time = 1.0, the output y = 0.0 (before event), 1.0 (after event)
e.g., time = 1.5, the output y = 2.5,
e.g., time = 2.0, the output y = 4.0,
e.g., time = 5.0, the output y = 23.0 (i.e., extrapolation via last 2 points).
The table matrix can be defined in the following ways:
tableName is "NoName" or has only blanks, fileName is "NoName" or has only blanks.
or Scilab by commandsave tables.mat tab1 tab2 tab3
when the three tables tab1, tab2, tab3 should be used from the model.savematfile tables.mat tab1 tab2 tab3
When the constant "NO_FILE_SYSTEM" is defined, all file I/O related parts of the source code are removed by the C-preprocessor, such that no access to files takes place.
If tables are read from a text file, the file needs to have the following structure ("-----" is not part of the file content):
----------------------------------------------------- #1 double tab1(6,2) # comment line 0 0 1 0 1 1 2 4 3 9 4 16 double tab2(6,2) # another comment line 0 0 2 0 2 2 4 8 6 18 8 32 -----------------------------------------------------
Note, that the first two characters in the file need to be "#1" (a line comment defining the version number of the file format). Afterwards, the corresponding matrix has to be declared with type (= "double" or "float"), name and actual dimensions. Finally, in successive rows of the file, the elements of the matrix have to be given. The elements have to be provided as a sequence of numbers in row-wise order (therefore a matrix row can span several lines in the file and need not start at the beginning of a line). Numbers have to be given according to C syntax (such as 2.3, -2, +2.e4). Number separators are spaces, tab (\t), comma (,), or semicolon (;). Several matrices may be defined one after another. Line comments start with the hash symbol (#) and can appear everywhere. Text files should either be ASCII or UTF-8 encoded, where UTF-8 encoded strings are only allowed in line comments and an optional UTF-8 BOM at the start of the text file is ignored. Other characters, like trailing non comments, are not allowed in the file.
MATLAB is a registered trademark of The MathWorks, Inc.
Release Notes: