Calculation of pressure loss in a straight pipe for turbulent flow regime of single-phase fluid flow only considering surface roughness.
This function shall be used within the restricted limits according to the referenced literature.
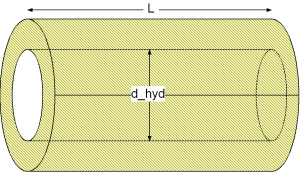
The pressure loss dp for straight pipes is determined by:
dp = lambda_FRI * (L/d_hyd) * (rho/2) * velocity^2
with
| lambda_FRI | as Darcy friction factor [-]. |
| L | as length of straight pipe [m], |
| d_hyd | as hydraulic diameter of straight pipe [m], |
| rho | as density of fluid [kg/m3], |
| velocity | as mean velocity [m/s]. |
The Darcy friction factor lambda_FRI for a straight pipe in the turbulent regime can be calculated for a smooth surface (Blasius law) or a rough surface (Colebrook-White law).
Smooth surface (roughness = Modelica.Fluid.Dissipation.Utilities.Types.Roughness.Neglected) w.r.t. Blasius law in the turbulent regime according to [Idelchik 2006, p. 77, sec. 15]:
lambda_FRI = 0.3164*Re^(-0.25)
with
| lambda_FRI | as Darcy friction factor [-]. |
| Re | as Reynolds number [-]. |
Note that the Darcy friction factor lambda_FRI for smooth straight pipes in the turbulent regime is independent of the surface roughness K .
Rough surface (roughness = Modelica.Fluid.Dissipation.Utilities.Types.Roughness.Considered) w.r.t. Colebrook-White law in the turbulent regime according to [Miller 1984, p. 191, eq. 8.4]:
lambda_FRI = 0.25/{lg[k/(3.7*d_hyd) + 5.74/(Re)^0.9]}^2
with
| d_hyd | as hydraulic diameter [-], |
| k= K/d_hyd | as relative roughness [-], |
| K | as roughness (average height of surface asperities [m]. |
| lambda_FRI | as Darcy friction factor [-], |
| Re | as Reynolds number [-]. |
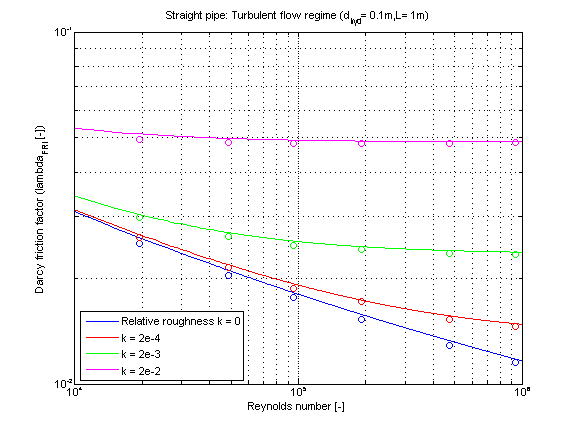
The Darcy friction factor lambda_FRI in dependence of Reynolds number for different values of relative roughness k is shown in the figure below.
Note that this pressure loss function shall not be used for the modelling outside of the turbulent flow regime at Re < 4e3 even though it could be used for that.
If the overall flow regime shall be modelled, the pressure loss function dp_overall can be used.