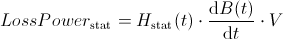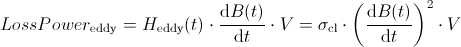Hysteresis power losses
The total power loss (LossPower) of an hysteresis
flux tube element is the sum of the power loss due to the static
ferromagnetic hysteresis (LossPowerStat) and the power
loss due to eddy currents (LossPowerEddy).
The two components LossPowerStat and
LossPowerEddy can be calculated as follows.
Where σcl is the classical eddy current
factor (see
UsersGuide.Hysteresis.DynamicHysteresis) and V the volume of
the core material. The equations show that
LossPowerStat acts as power sink and power source
(magnetic energy storage) whereas LossPowerEddy is
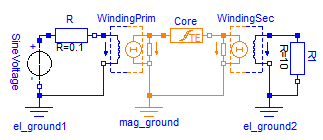
always positive (Power sink). By means of an simple example the
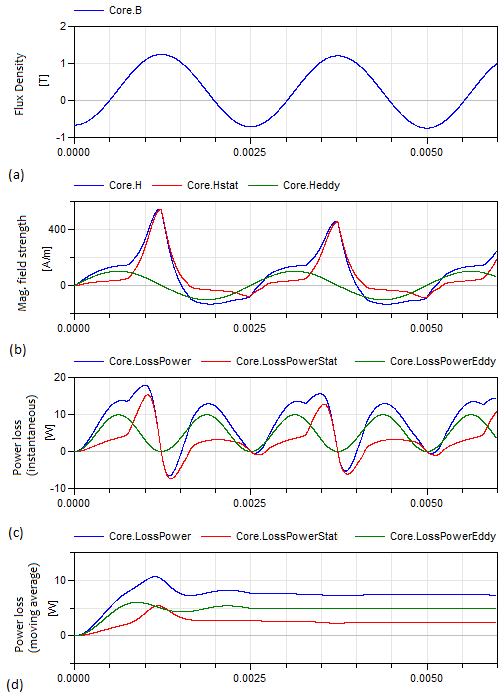
following figures show the time course of the magnetic flux
density, the magnetic field strength and the hysteresis losses. The
pulsating course of the power loss (see Fig. 3c) makes it difficult
to estimate an average loss. For this reason, the hysteresis flux
tube elements are capable of directly computing the moving average
of the power losses. Therefore, t_avg of the
"LossesAndHeat" tab of the elements parameter dialog may be
adjusted to set an adequate time interval (see Fig. 3d).
Fig. 2: Simulated total
dynamic hysteresis loop with its static and eddy current
fractions
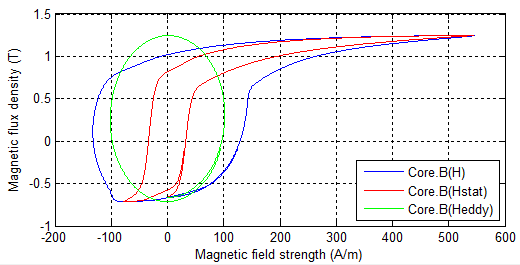 |
Fig. 3: Simulated outputs
of the Core component of Fig. 1
 |
Generated at 2020-06-05T21:39:08Z by OpenModelica 1.16.0~dev-442-g2e5bc9f