This salient air gap model can be used for machines with uniform air gaps and for machines with rotor saliency. The air gap model is not symmetrical towards stator and rotor since it is assumed the saliency always refers to the rotor. The saliency of the air gap is represented by a main field inductance in the d- and q-axis.
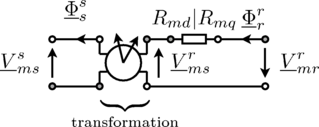
For the mechanical interaction of the air gap model with the
stator and the rotor is equipped with two rotational
connectors. The torques acting on both connectors have the same
absolute values but different signs. The difference between the
stator and the rotor angle, 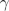 , is required for the transformation of the magnetic stator
quantities to the rotor side.
, is required for the transformation of the magnetic stator
quantities to the rotor side.
The air gap model has two magnetic stator and two magnetic rotor ports. The magnetic potential difference and the magnetic flux of the stator (superscript s) are transformed to the rotor fixed reference frame (superscript r). The effective reluctances of the main field with respect to the d- and q-axis are considered then in the balance equations
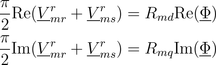
according to the following figure.
 |
SinglePhaseWinding, SymmetricPolyphaseWinding, SymmetricPolyphaseCageWinding SaliencyCageWinding