The admittance model represents a parallel
connection of a conductor and either a capacitor or inductor.
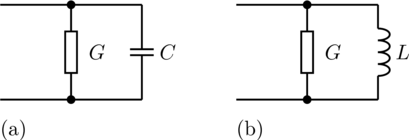
The linear admittance connects the complex voltage
v with the complex current
i by v*Y = i.
The admittance Y_ref = G_ref + j*B_ref is given as
complex input signal, representing the resistive and reactive
component of the input admittance. The resistive component is
modeled temperature dependent, so the real part G_actual =
real(Y) is determined from the actual operating
temperature and the reference input conductance
real(Y_ref). The reactive component B_actual =
imag(Y) is equal to imag(Y_ref) if
frequencyDependent = false. Frequency dependency is
considered by frequencyDependent = true,
distinguishing two cases:
imag(Y_ref) > 0: capacitive caseB_actual is proportional to
f/f_refimag(Y_ref) < 0: inductive caseB_actual is proportional to
f_ref/fA zero crossing of the real or imaginary part of the admittance
signal Y_ref could cause singularities due to the
actual structure of the connected network.
Resistor, Conductor, Capacitor, Inductor, Impedance, Admittance, Variable resistor, Variable conductor, Variable capacitor, Variable inductor, Variable impedance