Constants and types with choices, especially to build menus
In this package types and constants are defined that are used in the MultiBody library. The types have additional annotation choices definitions that define the menus to be built up in the graphical user interface when the type is used as parameter in a declaration.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.TypesPackage (Icon for packages containing type definitions).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Axis vector with choices | |
| Label of axis with choices | |
| Sequence of planar frame rotations with choices | |
| RGB representation of color | |
| RGB representation of color as Real type | |
| Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) | |
| Type of shape (box, sphere, cylinder, pipecylinder, cone, pipe, beam, gearwheel, spring, <external shape>) | |
| Type of the additional data that can be defined for an elementary ShapeType | |
| Enumeration to define the frame in which an absolute vector is resolved (world, frame_a, frame_resolve) | |
| Enumeration to define the frame in which an absolute vector is resolved (world, frame_b, frame_resolve) | |
| Enumeration to define the frame in which a relative vector is resolved (world, frame_a, frame_b, frame_resolve) | |
| Enumeration defining in which way the fixed orientation of frame_b with respect to frame_a is specified | |
| Enumeration defining the type of the gravity field | |
| Enumeration defining the kind of physical quantity represented by the vector | |
| Default settings of the MultiBody library via constants |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.Axis
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.AxisAxis vector with choices
Type definition of an axis vector with scroll down menu that provides the most often used axes vectors along the coordinate axes of a frame. For an example see parameter "n" in model Joints.Revolute.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.TypeReal (Icon for Real types).
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Custom Parameters | |
| unit | "1" |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.AxisLabel
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.AxisLabelLabel of axis with choices
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.RotationSequence
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.RotationSequenceSequence of planar frame rotations with choices
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Custom Parameters | |
| min | {1,1,1} |
| max | {3,3,3} |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.Color
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.ColorRGB representation of color
Type Color is an Integer vector with 3 elements, {r, g, b}, and specifies the color of a shape. {r, g, b} are the "red", "green" and "blue" color parts. Note, r, g and b are given in the range 0 … 255.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.TypeInteger (Icon for Integer types).
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Custom Parameters | |
| min | 0 |
| max | 255 |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.RealColor
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.RealColorRGB representation of color as Real type
Type RealColor is a Real vector with 3 elements, {r, g, b}, and specifies the color of a shape. {r,g,b} are the "red", "green" and "blue" color parts. Note, r, g and b are given in the range 0 … 255.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.TypeReal (Icon for Real types).
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Custom Parameters | |
| min | 0 |
| max | 255 |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.SpecularCoefficient
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.SpecularCoefficientReflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed)
Type SpecularCoefficient defines the reflection of ambient light on shape surfaces. If value = 0, the light is completely absorbed. Often, 0.7 is a reasonable value. It might be that from some viewing directions, a body is no longer visible, if the SpecularCoefficient value is too high. In the following image, the different values of SpecularCoefficient are shown for a cylinder:
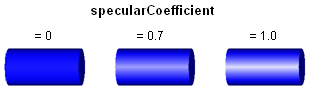
Extends from Modelica.Icons.TypeReal (Icon for Real types).
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Custom Parameters | |
| min | 0 |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.ShapeType
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.ShapeTypeType of shape (box, sphere, cylinder, pipecylinder, cone, pipe, beam, gearwheel, spring, <external shape>)
Type ShapeType is used to define the shape of the visual object as parameter String. Usually, "shapeType" is used as instance name. The following values for shapeType are possible, e.g., shapeType="box":
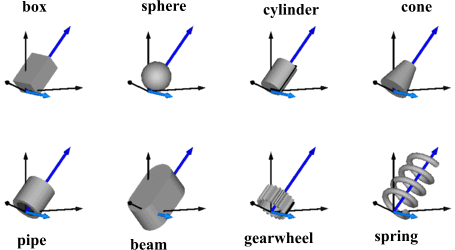
The dark blue arrows in the figure above are directed along variable lengthDirection. The light blue arrows are directed along variable widthDirection. The coordinate systems in the figure represent frame_a of the Shape component.
Additionally, external shapes can be specified as (not all options might be supported by all tools):
The supported file formats are tool dependent. Most tools support at least DXF-files (a tool might support 3-dim. Face of the DXF format only), but may support other format as well (such as stl, obj, 3ds). Since visualization files contain color and other data, the corresponding information in the model is usually ignored.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.TypeString (Icon for String types).
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.ShapeExtra
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Types.ShapeExtraType of the additional data that can be defined for an elementary ShapeType
This type is used in shapes of visual objects to define extra data depending on the shape type. Usually, input variable extra is used as instance name:
| shapeType | Meaning of parameter extra |
|---|---|
| "cylinder" | if extra > 0, a black line is included in the cylinder to show the rotation of it. |
| "cone" | extra = diameter-left-side / diameter-right-side, i.e., extra = 1: cylinder extra = 0: "real" cone. |
| "pipe" | extra = outer-diameter / inner-diameter, i.e, extra = 1: cylinder that is completely hollow extra = 0: cylinder without a hole. |
| "gearwheel" | extra is the number of teeth of the (external) gear. If extra < 0, an internal gear is visualized with |extra| teeth. The axis of the gearwheel is along "lengthDirection", and usually: width = height = 2*radiusOfGearWheel. |
| "spring" | extra is the number of windings of the spring. Additionally, "height" is not the "height" but 2*coil-width. |
| external shape | extra = 0: Visualization from file is not scaled. extra = 1: Visualization from file is scaled with "length", "width" and "height" of the shape |
Extends from Modelica.Icons.TypeReal (Icon for Real types).
Enumeration to define the frame in which an absolute vector is resolved (world, frame_a, frame_resolve)
| Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve (frame_resolve must be connected) |
Enumeration to define the frame in which an absolute vector is resolved (world, frame_b, frame_resolve)
| Types.ResolveInFrameB. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_b | Resolve vector in frame_b |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve (frame_resolve must be connected) |
Enumeration to define the frame in which a relative vector is resolved (world, frame_a, frame_b, frame_resolve)
| Types.ResolveInFrameAB. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_b | Resolve vector in frame_b |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve (frame_resolve must be connected) |
Enumeration defining in which way the fixed orientation of frame_b with respect to frame_a is specified
| Types.RotationTypes. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| RotationAxis | frame_b is defined by rotating the coordinate system along an axis fixed in frame_a and with a fixed angle. |
| TwoAxesVectors | frame_b is defined by resolving two vectors of frame_b in frame_a. |
| PlanarRotationSequence | frame_b is defined by rotating the coordinate system along 3 consecutive axes vectors with fixed rotation angles (e.g., Cardan or Euler angle sequence rotation). |
Enumeration defining the type of the gravity field
| Types.GravityTypes. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NoGravity | No gravity field |
| UniformGravity | Gravity field is described by a vector of constant gravity acceleration |
| PointGravity | Central gravity field. The gravity acceleration vector is directed to the field center and the gravity is proportional to 1/r^2, where r is the distance to the field center. |
Enumeration defining the kind of physical quantity represented by the vector
| Types.VectorQuantity. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Force | Vector represents a force quantity |
| Torque | Vector represents a torque quantity |
| Velocity | Vector represents a velocity quantity |
| Acceleration | Vector represents an acceleration quantity |
| AngularVelocity | Vector represents an angular velocity quantity |
| AngularAcceleration | Vector represents an angular acceleration quantity |
| RelativePosition | Vector represents the relative position |