kc_overall |
|
Information
This information is part of the Modelica Standard Library maintained by the Modelica Association.
Calculation of mean convective heat transfer coefficient kc of a straight pipe at an uniform wall temperature or uniform heat flux and for a hydrodynamically developed or undeveloped laminar or turbulent fluid flow with neglect or consideration of pressure loss influence.
Functions kc_overall and kc_overall_KC
There are basically three differences:
- The function kc_overall is using kc_overall_KC but offers additional output variables like e.g. Reynolds number or Nusselt number and failure status (an output of 1 means that the function is not valid for the inputs).
- Generally the function kc_overall_KC is numerically best used for the calculation of the mean convective heat transfer coefficient kc at known mass flow rate.
- You can perform an inverse calculation from kc_overall_KC, where an unknown mass flow rate is calculated out of a given mean convective heat transfer coefficient kc
Restriction
- circular cross sectional area
- uniform wall temperature (UWT) or uniform heat flux (UHF)
- hydrodynamically developed fluid flow
- hydraulic diameter / length ≤ 1
- 0.6 ≤ Prandtl number ≤ 1000
Geometry and Calculation
This heat transfer function enables a calculation of heat transfer coefficient for laminar and turbulent flow regime. The geometry, constant and fluid parameters of the function are the same as for kc_laminar and kc_turbulent.
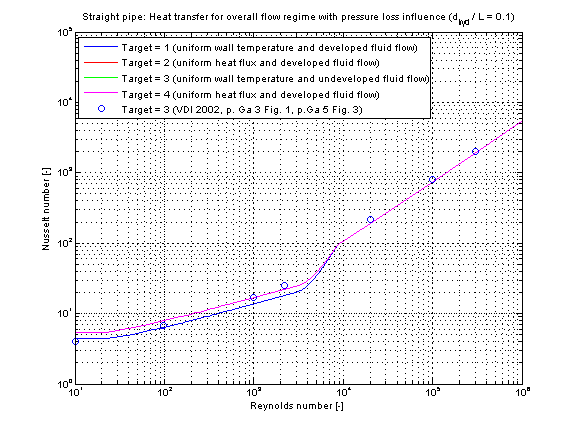
The calculation conditions for laminar and turbulent flow is equal to the calculation in kc_laminar and kc_turbulent. A smooth transition between both functions is carried out between 2200 ≤ Re ≤ 10000 (see figure below).
Verification
The mean Nusselt number Nu representing the mean convective heat transfer coefficient kc is shown for the fluid properties of Water (Prandtl number Pr = 7) and a diameter to pipe length fraction of 0.1 in the figure below.
The following verification considers pressure loss influence (roughness =2).
References
- Bejan,A.:
- Heat transfer handbook. Wiley, 2003.
- VDI:
- VDI - Wärmeatlas: Berechnungsblätter für den Wärmeübergang. Springer Verlag, 9th edition, 2002.