Library of mathematical functions (e.g., sin, cos) and of functions operating on vectors and matrices
This package contains basic mathematical functions (such as sin(..)), as well as functions operating on vectors, matrices, nonlinear functions, and Boolean vectors.
Martin Otter
and Marcus Baur
Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V. (DLR)
Institut für Systemdynamik und Regelungstechnik (DLR-SR)
Forschungszentrum Oberpfaffenhofen
D-82234 Wessling
Germany
email: Martin.Otter@dlr.de
Copyright © 1998-2020, Modelica Association and contributors
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Package (Icon for standard packages).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Library of functions operating on vectors | |
| Library of functions operating on Boolean vectors | |
| Library of functions operating on matrices | |
| Library of functions operating on nonlinear equations | |
| Library of functions operating on polynomials (including polynomial fitting) | |
| Library of functions for generating random numbers | |
| Library of distribution functions | |
| Library of special mathematical functions | |
| Library of functions for the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) | |
| Icons for Math | |
| Determine if two Real scalars are numerically identical | |
| Determine if the integer input is a power of 2 | |
| Sine | |
| Cosine | |
| Tangent (u shall not be -pi/2, pi/2, 3*pi/2, ...) | |
| Inverse sine (-1 <= u <= 1) | |
| Inverse cosine (-1 <= u <= 1) | |
| Inverse tangent | |
| Four quadrant inverse tangent | |
| Four quadrant inverse tangent (select solution that is closest to given angle y0) | |
| Hyperbolic sine | |
| Hyperbolic cosine | |
| Hyperbolic tangent | |
| Inverse of sinh (area hyperbolic sine) | |
| Inverse of cosh (area hyperbolic cosine) | |
| Exponential, base e | |
| Natural (base e) logarithm (u shall be > 0) | |
| Base 10 logarithm (u shall be > 0) | |
| Wrap angle to interval ]-pi,pi] or [0,2*pi[ |
 Modelica.Math.isEqual
Modelica.Math.isEqualDetermine if two Real scalars are numerically identical
Math.isEqual(s1, s2); Math.isEqual(s1, s2, eps=0);
The function call "Math.isEqual(s1, s2)" returns true,
if the two Real scalars s1 and s2 are identical. Otherwise the function
returns false. The equality check is performed by
"abs(s1-s2) ≤ eps", where "eps"
can be provided as third argument of the function. Default is "eps = 0".
Real s1 = 2.0; Real s2 = 2.0; Real s3 = 2.000001; Boolean result; algorithm result := Math.isEqual(s1,s2); // = true result := Math.isEqual(s1,s3); // = false result := Math.isEqual(s1,s3,0.1); // = true
Vectors.isEqual, Matrices.isEqual, Strings.isEqual
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Function (Icon for functions).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| s1 | First scalar |
| s2 | Second scalar |
| eps | The two scalars are identical if abs(s1-s2) <= eps |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result | = true, if scalars are identical |
 Modelica.Math.isPowerOf2
Modelica.Math.isPowerOf2Determine if the integer input is a power of 2
Math.isPowerOf2(i);
The function call "Math.isPowerOf2(i)" returns true,
if the Integer input i is a power of 2. Otherwise the function
returns false. The Integer input has to be >=1.
Integer i1 = 1; Integer i2 = 4; Integer i3 = 9; Boolean result; algorithm result := Math.isPowerOf2(i1); // = true 2^0 result := Math.isPowerOf2(i2); // = true 2^2 result := Math.isPowerOf2(i3); // = false
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Function (Icon for functions).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| i | Integer scalar |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result | = true, if integer scalar is a power of 2 |
 Modelica.Math.sin
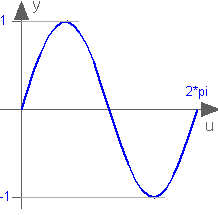
Modelica.Math.sinSine
This function returns y = sin(u), with -∞ < u < ∞:
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisLeft (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis on left side).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable [rad] |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=sin(u) |
 Modelica.Math.cos
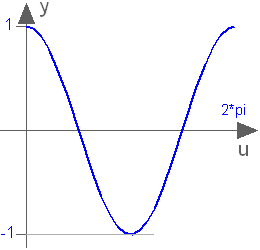
Modelica.Math.cosCosine
This function returns y = cos(u), with -∞ < u < ∞:
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisLeft (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis on left side).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable [rad] |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=cos(u) |
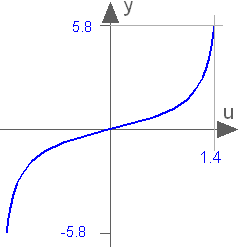
 Modelica.Math.tan
Modelica.Math.tanTangent (u shall not be -pi/2, pi/2, 3*pi/2, ...)
This function returns y = tan(u), with -∞ < u < ∞ (if u is a multiple of (2n-1)*pi/2, y = tan(u) is +/- infinity).
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable [rad] |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=tan(u) |
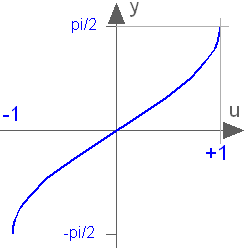
 Modelica.Math.asin
Modelica.Math.asinInverse sine (-1 <= u <= 1)
This function returns y = asin(u), with -1 ≤ u ≤ +1:
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=asin(u) [rad] |
 Modelica.Math.acos
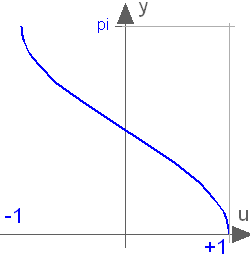
Modelica.Math.acosInverse cosine (-1 <= u <= 1)
This function returns y = acos(u), with -1 ≤ u ≤ +1:
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=acos(u) [rad] |
 Modelica.Math.atan
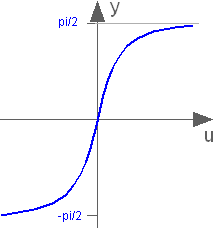
Modelica.Math.atanInverse tangent
This function returns y = atan(u), with -∞ < u < ∞:
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=atan(u) [rad] |
 Modelica.Math.atan2
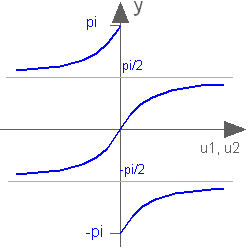
Modelica.Math.atan2Four quadrant inverse tangent
This function returns y = atan2(u1,u2) such that tan(y) = u1/u2 and y is in the range -pi < y ≤ pi. u2 may be zero, provided u1 is not zero. Usually u1, u2 is provided in such a form that u1 = sin(y) and u2 = cos(y):
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u1 | First independent variable |
| u2 | Second independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=atan2(u1, u2)=atan(u1/u2) [rad] |
 Modelica.Math.atan3
Modelica.Math.atan3Four quadrant inverse tangent (select solution that is closest to given angle y0)
This function returns y = atan3(u1,u2,y0) such that
tan(y) = u1/u2 and
y is in the range: -pi < y-y0 ≤ pi.
u2 may be zero, provided u1 is not zero. The difference to
Modelica.Math.atan2(..) is the optional third argument y0 that
allows to specify which of the infinite many solutions
shall be returned:
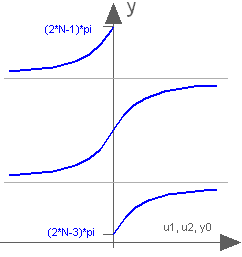
Note, for the default case (y0=0), exactly the same result as with atan2(..) is returned.
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u1 | First independent variable |
| u2 | Second independent variable |
| y0 | y shall be in the range: -pi < y-y0 <= pi [rad] |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=atan3(u1, u2, y0)=atan(u1/u2) [rad] |
 Modelica.Math.sinh
Modelica.Math.sinhHyperbolic sine
This function returns y = sinh(u), with -∞ < u < ∞:
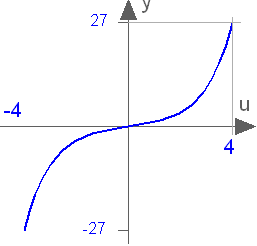
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=sinh(u) |
 Modelica.Math.cosh
Modelica.Math.coshHyperbolic cosine
This function returns y = cosh(u), with -∞ < u < ∞:
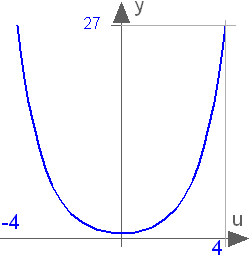
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=cosh(u) |
 Modelica.Math.tanh
Modelica.Math.tanhHyperbolic tangent
This function returns y = tanh(u), with -∞ < u < ∞:
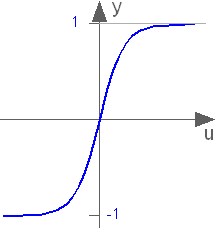
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=tanh(u) |
 Modelica.Math.asinh
Modelica.Math.asinhInverse of sinh (area hyperbolic sine)
The function returns the area hyperbolic sine of its input argument u. This inverse of sinh(..) is unique and there is no restriction on the input argument u of asinh(u) (-∞ < u < ∞):
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=asinh(u) |
 Modelica.Math.acosh
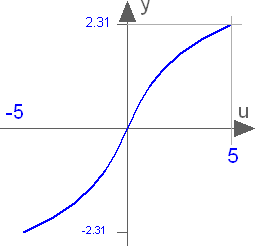
Modelica.Math.acoshInverse of cosh (area hyperbolic cosine)
This function returns the area hyperbolic cosine of its input argument u. The valid range of u is
+1 ≤ u < +∞
If the function is called with u < 1, an error occurs. The function cosh(u) has two inverse functions (the curve looks similar to a sqrt(..) function). acosh(..) returns the inverse that is positive. At u=1, the derivative dy/du is infinite. Therefore, this function should not be used in a model, if u can become close to 1:
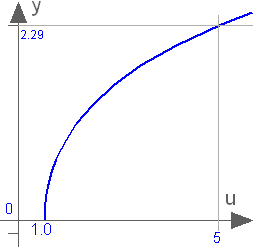
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisLeft (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis on left side).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=acosh(u) |
 Modelica.Math.exp
Modelica.Math.expExponential, base e
This function returns y = exp(u), with -∞ < u < ∞:
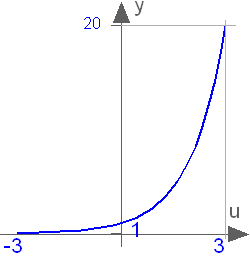
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=exp(u) |
 Modelica.Math.log
Modelica.Math.logNatural (base e) logarithm (u shall be > 0)
This function returns y = log(10) (the natural logarithm of u), with u > 0:
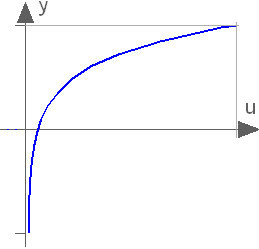
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisLeft (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis on left side).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=ln(u) |
 Modelica.Math.log10
Modelica.Math.log10Base 10 logarithm (u shall be > 0)
This function returns y = log10(u), with u > 0:
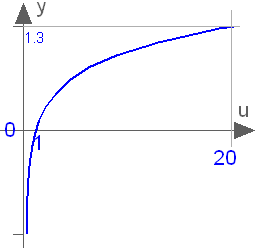
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisLeft (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis on left side).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Independent variable |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Dependent variable y=lg(u) |
 Modelica.Math.wrapAngle
Modelica.Math.wrapAngleWrap angle to interval ]-pi,pi] or [0,2*pi[
This function wraps the input angle u to the interval ]-pi,pi], if positiveRange == false.
Otherwise the input angle u is wrapped to the interval [0,2*pi[.
Extends from Modelica.Math.Icons.AxisCenter (Basic icon for mathematical function with y-axis in the center).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| u | Input angle [rad] |
| positiveRange | Use only positive output range, if true |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Wrapped output angle [rad] |