 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide
Library Translational is a free Modelica package providing 1-dimensional, translational mechanical components to model in a convenient way translational mechanical systems. More details are given in the following sub-sections:
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Information (Icon for general information packages).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Flange Connectors | |
| Support Forces | |
| Sign Conventions | |
| User Defined Components | |
| State Selection | |
| Contact |
 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.Overview
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.OverviewThis package contains components to model 1-dimensional translational mechanical systems, including different types of masses, external forces, spring/damper elements, frictional elements, elastogaps, elements to measure position, velocity, acceleration or the cut-force of a flange. In sublibrary Examples several examples are present to demonstrate the usage of the elements. Just open the corresponding example model and simulate the model according to the provided description.
A unique feature of this library is the component-oriented modeling of Coulomb friction elements, such as support friction. Even (dynamically) coupled friction elements can be handled without introducing stiffness, which leads to fast simulations. The underlying theory is based on the solution of mixed continuous/discrete systems of equations, i.e., equations where the unknowns are of type Real, Integer or Boolean. Provided appropriate numerical algorithms for the solution of such types of systems are available in the simulation tool, the simulation of (dynamically) coupled friction elements of this library is efficient and reliable.
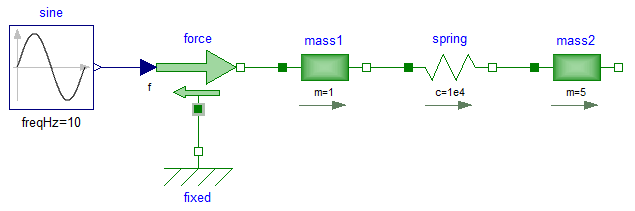
A simple example of the usage of this library is given in the
figure above. This model consists of a mass1 with mass m = 1 kg which
is connected via a spring to a mass2 with mass m = 5 kg.
The left mass is driven via an external, sinusoidal force.
The filled and non-filled green squares at the left and
right side of a component represent mechanical flanges.
Drawing a line between such squares means that the corresponding
flanges are rigidly attached to each other.
By convention in this library, the connector characterized as a
filled green square is called flange_a and placed at the
left side of the component in the "design view" and the connector
characterized as a non-filled green square is called flange_b
and placed at the right side of the component in the "design view".
The two connectors are completely identical, with the only
exception that the graphical layout is a little bit different in order
to distinguish them for easier access of the connector variables.
For example, mass1.flange_a.f is the cut-force in the connector
flange_a of component mass1.
The components of this library can be connected together in an arbitrary way. E.g., it is possible to connect two springs or two shafts with mass directly together, see figure below.
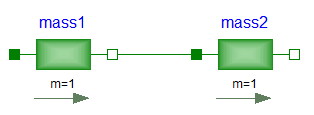
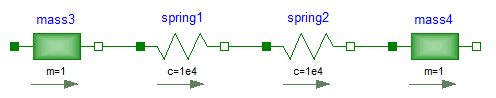
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Information (Icon for general information packages).
 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.FlangeConnectors
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.FlangeConnectorsA flange is described by the connector class Flange_a or Flange_b. As already noted in section Overview, the two connector classes are completely identical. There is only a difference in the icons, in order to easier identify a flange variable in a diagram. Both connector classes contain the following variables:
SI.Position s "Absolute position of flange"; flow SI.Force f "Cut force directed into flange";
If needed, the velocity v and the
acceleration a of a flange connector can be
determined by differentiation of the flange position s:
v = der(s); a = der(v);
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Information (Icon for general information packages).
 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.SupportForces
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.SupportForcesThe following figure shows examples of components equipped with a support flange (framed flange in the lower center), which can be used to fix components on the ground or on other moving elements or to combine them with force elements. Via Boolean parameter useSupport, the support flange is enabled or disabled. If it is enabled, it must be connected. If it is disabled, it needs not be connected.
Depending on the setting of useSupport, the icon of the corresponding component is changing, to either show the support flange or a ground mounting. For example, the two implementations in the following figure give identical results.
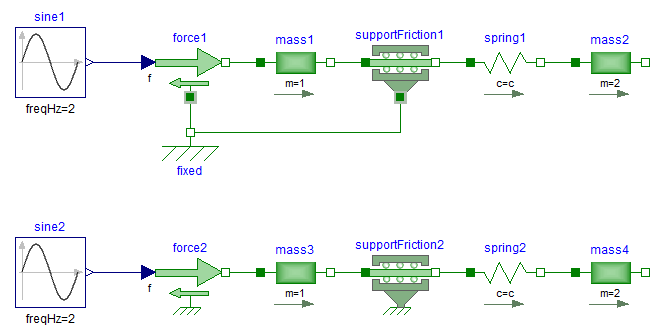
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Information (Icon for general information packages).
 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.SignConventions
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.SignConventionsThe variables of a component of this library can be accessed in the usual way. However, since most of these variables are basically elements of vectors, i.e., have a direction, the question arises how the signs of variables shall be interpreted. The basic idea is explained at hand of the following figure:
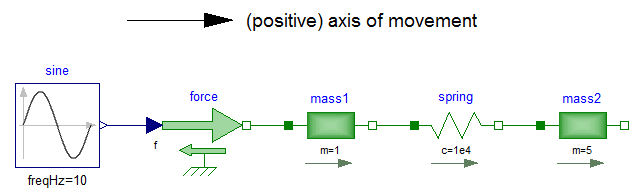
First, one has to define a positive direction of this line, called axis of movement. In the top of the figure this is characterized by an arrow and a corresponding text. The simple rule is now: If a variable of a component is positive and can be interpreted as the element of a vector (e.g., force or velocity vector), the corresponding vector is directed into the positive direction of the axis of movement. In the following figure, the right-most mass of the figure above is displayed with the positive vector direction displayed according to this rule:
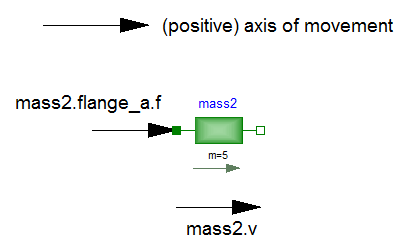
The cut-force mass2.flange_a.f
of the right mass is directed into the
direction of movement if the values are positive. Similarly,
the velocity mass2.v of the right mass
is also directed into the
direction of movement if the values are positive
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Information (Icon for general information packages).
 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.UserDefinedComponents
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.UserDefinedComponentsIn this section some hints are given to define your own 1-dimensional translational components which are compatible with the elements of this package. It is convenient to define a new component by inheritance from one of the following base classes, which are defined in sublibrary Interfaces:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PartialCompliant | Compliant connection of two translational 1-dim. flanges (used for force laws such as a spring or a damper). |
| PartialCompliantWithRelativeStates | Same as "PartialCompliant", but relative position and relative speed are defined as preferred states. Use this partial model if the force law needs anyway the relative speed. The advantage is that it is usually better to use relative positions between drive train components as states, especially, if the position is not limited. |
| PartialElementaryTwoFlangesAndSupport2 | Partial model for a 1-dim. translational component consisting of the flange of an input shaft, the flange of an output shaft and the support. |
| PartialForce | Partial model of an external force acting at the flange (accelerates the flange). |
| PartialTwoFlanges | General connection of two translational 1-dim. flanges. |
| PartialAbsoluteSensor | Measure absolute flange variables. |
| PartialRelativeSensor | Measure relative flange variables. |
The difference between these base classes are the auxiliary variables defined in the model and the relations between the flange variables already defined in the base class. For example, in model PartialCompliant there is no support flange, whereas in model PartialElementaryTwoFlangesAndSupport2 there is a support flange.
The equations of a mechanical component are vector equations, i.e., they need to be expressed in a common coordinate system. Therefore, a local axis of movement has to be defined for a component. All vector quantities, such as cut-forces or velocities have to be expressed according to this definition. Examples for such a definition are given in the following figure for a mass component:
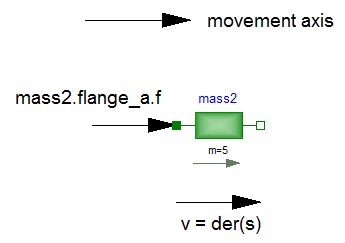
As can be seen, all vectors are directed into the direction of the movement axis. The positions in the flanges are defined correspondingly.
On first view, one may assume that the selected local coordinate system has an influence on the usage of the component. But this is not the case, as shown in the next figure:
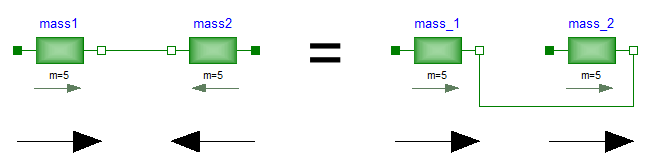
In the figure, the local axes of translation of the components
are shown. The connection of two masses in the left and in the
right part of the figure are completely equivalent, i.e., the right
part is just a different drawing of the left part. This is due to the
fact, that by a connection, the two local coordinate systems are
made identical and the (automatically) generated connection equations
(= positions are identical, cut-forces sum-up to zero) are also
expressed in this common coordinate system. Therefore, even if in
the left figure it seems to be that the velocity vector of
mass2 goes from right to left, in reality it goes from
left to right as shown in the right part of the figure, where the
local coordinate systems are drawn such that they are aligned.
Note, that the simple rule stated in section
Sign conventions
also determines that
the velocity of mass2 in the left part of the
figure is directed from left to right.
To summarize, the local coordinate system selected for a component is just necessary in order that the equations of this component are expressed correctly. The selection of the coordinate system is arbitrary and has no influence on the usage of the component. Especially, the actual direction of, e.g., a cut-force is most easily determined by the rule of section Sign conventions. A more strict determination by aligning coordinate systems and then using the vector direction of the local coordinate systems, often requires a re-drawing of the diagram and is therefore less convenient to use.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Information (Icon for general information packages).
 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.StateSelection
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.StateSelectionOnly a few components of the Translational library use the der(…) operator and are therefore candidates to have states. Most important, component Mass defines the absolute position and the absolute velocity of this component as candidate for states. In the "Advanced" menu the built-in StateSelect enumeration can be set to define the priority to use these variables as states. Without further action, in most cases a tool will select these variables as states.
For positioning drive trains where the goal is to position a load, the absolute positions of the components are bounded, and the issue discussed below is not present.
For drive trains where the goal is to control the velocity of a load, the absolute positions of the components are quickly increasing during operation. This is critical, because then the step size control of time integrators might no longer work appropriately.
Integrators with step size control adjust their time step size automatically to meet user defined error bounds ("tolerances"). Typically the local error estimate ESTi is compared with a mixed bound for absolute and relative errors.
EST_i ≤ abstol_i + reltol_i*|x_i|
Here, abstoli and reltoli denote the bounds for the absolute and relative error of state variable xi, respectively. This mixed error bound is used since it is more robust than a pure relative error based error bound if the nominal value xi is (very) close to 0. In a Modelica simulation model, typically the same relative tolerance reltol is used for all states and the absolute tolerances are computed using the relative tolerance and the nominal values of the states:
reltol_i = reltol abstol_i = reltol*x_i(nominal)*0.01
This error control fails if the state variable xi grows without bounds (such as for a drive train), since then the allowed error also grows without bounds. The effect is that the error control on this variable is practically switched off. The correct way to handle this would be to set reltoli = 0 on such a state variable and only use an absolute tolerance for the step size control.
At the time of the library design, there was not yet a possibility to provide this information in Modelica. In order to reduce this effect, it is advisable to not use absolute positions, but relative positions as states. A user can define relative variables as states explicitly with component RelativeStates. Furthermore, all compliant components, such as SpringDamper are defining the relative position and the relative velocity as preferred states. Therefore, a tool will select in most cases relative positions as states.
The relative positions of compliant components are usually small. Without further action, the error control would not work properly on variables that are so small (so often switching the error control off). The remedy is to define explicitly a nominal value on the relative position. This definition is provided in the "Advanced" menu of the compliant components with parameter "s_nominal". The default value is 1e-4 m, to be in the order of a compliant deformation of a drive.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Information (Icon for general information packages).
 Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.Contact
Modelica.Mechanics.Translational.UsersGuide.ContactFor current information on library officers please refer to the main Contact section.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.Contact (Icon for contact information).
Automatically generated Thu Oct 1 16:07:55 2020.