Sensors to measure variables
Package Sensors contains ideal measurement components to determine absolute and relative kinematic quantities, as well as cut-forces, cut-torques and power. All measured quantities can be provided in every desired coordinate system.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.SensorsPackage (Icon for packages containing sensors).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Measure absolute kinematic quantities of frame connector | |
| Measure relative kinematic quantities between two frame connectors | |
| Measure absolute position vector of the origin of a frame connector | |
| Measure absolute velocity vector of origin of frame connector | |
| Measure absolute angles between frame connector and the world frame | |
| Measure absolute angular velocity of frame connector | |
| Measure relative position vector between the origins of two frame connectors | |
| Measure relative velocity vector between the origins of two frame connectors | |
| Measure relative angles between two frame connectors | |
| Measure relative angular velocity between two frame connectors | |
| Measure the distance between the origins of two frame connectors | |
| Measure cut force vector | |
| Measure cut torque vector | |
| Measure cut force and cut torque vector | |
| Measure power flowing from frame_a to frame_b | |
| Transform absolute vector in to another frame | |
| Transform relative vector in to another frame | |
| Internal package, should not be used by user |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteSensor
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteSensorMeasure absolute kinematic quantities of frame connector
Absolute kinematic quantities of frame_a are determined and provided at the conditional output signal connectors. For example, if parameter "get_r = true", the connector "r" is enabled and contains the absolute vector from the world frame to the origin of frame_a. The following quantities can be provided as output signals:
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame a vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vectors in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vectors in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vectors in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and the vectors are resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
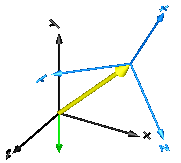
In the following figure the animation of an AbsoluteSensor component is shown. The light blue coordinate system is frame_a and the yellow arrow is the animated sensor.
Velocity, acceleration, angular velocity and angular acceleration are determined by differentiating them in the world frame and then transforming them in to the frame defined by resolveInFrame.
For example, if resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_a, then
v0 = der(frame_a.r0); v = resolve2(frame_a.R, v0);
is returned, i.e., the derivative of the absolute distance from the world frame to the origin of frame_a, resolved in frame_a.
The cut-force and the cut-torque in frame_resolve are always zero, whether frame_resolve is connected or not.
If get_angles = true, the 3 angles to rotate the world frame into frame_a along the axes defined by parameter sequence are returned. For example, if sequence = {3,1,2} then the world frame is rotated around angles[1] along the z-axis, afterwards it is rotated around angles[2] along the x-axis, and finally it is rotated around angles[3] along the y-axis and is then identical to frame_a. The 3 angles are returned in the range
-π <= angles[i] <= π
There are two solutions for "angles[1]" in this range. Via parameter guessAngle1 (default = 0) the returned solution is selected such that |angles[1] - guessAngle1| is minimal. The absolute transformation matrix of frame_a may be in a singular configuration with respect to "sequence", i.e., there is an infinite number of angle values leading to the same absolute transformation matrix. In this case, the returned solution is selected by setting angles[1] = guessAngle1. Then angles[2] and angles[3] can be uniquely determined in the above range.
The parameter sequence has the restriction that only values 1,2,3 can be used and that sequence[1] ≠ sequence[2] and sequence[2] ≠ sequence[3]. Often used values are:
sequence = {1,2,3} // Cardan or Tait-Bryan angle sequence
= {3,1,3} // Euler angle sequence
= {3,2,1}
Extends from Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.Internal.PartialAbsoluteSensor (Base class for absolute sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| animation | = true, if animation shall be enabled (show arrow) |
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which vectors are resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| get_r | = true, to measure the absolute position vector of the origin of frame_a |
| get_v | = true, to measure the absolute velocity of the origin of frame_a |
| get_a | = true, to measure the absolute acceleration of the origin of frame_a |
| get_w | = true, to measure the absolute angular velocity of frame_a |
| get_z | = true, to measure the absolute angular acceleration of frame_a |
| 3 angles to rotate the world frame into frame_a along the axes defined in "sequence" | |
| get_angles | = true, to measure the 3 rotation angles |
| sequence | If get_angles=true: Angles are returned to rotate world frame around axes sequence[1], sequence[2] and finally sequence[3] into frame_a |
| guessAngle1 | If get_angles=true: Select angles[1] such that abs(angles[1] - guessAngle1) is a minimum [rad] |
| Animation | |
| if animation = true | |
| arrowColor | Color of absolute arrow from world frame to frame_b |
| specularCoefficient | Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| r[3] | Absolute position vector frame_a.r_0 resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [m] |
| v[3] | Absolute velocity vector [m/s] |
| a[3] | Absolute acceleration vector [m/s2] |
| angles[3] | Angles to rotate world frame into frame_a via 'sequence' [rad] |
| w[3] | Absolute angular velocity vector [1/s] |
| z[3] | Absolute angular acceleration vector [1/s2] |
| frame_a | Coordinate system a of which the absolute kinematic quantities are measured |
| frame_resolve | If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_resolve, the output signals are resolved in this frame |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeSensor
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeSensorMeasure relative kinematic quantities between two frame connectors
Relative kinematic quantities between frame_a and frame_b are determined and provided at the conditional output signal connectors. For example, if parameter "get_r_rel = true", the connector "r_rel" is enabled and contains the relative vector from frame_a to frame_b. The following quantities can be provided as output signals:
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame a vector is resolved (before differentiation):
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vectors in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vectors in frame_a |
| frame_b | Resolve vectors in frame_b |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vectors in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and the vectors are resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
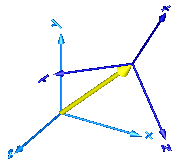
In the following figure the animation of a RelativeSensor component is shown. The light blue coordinate system is frame_a, the dark blue coordinate system is frame_b, and the yellow arrow is the animated sensor.
Note, derivatives of relative kinematic quantities are always performed with respect to the frame, in which the vector to be differentiated is resolved. After differentiation, it is possible via parameter resolveInFrameAfterDifferentiation (in the "Advanced" menu) to resolve the differentiated vector in another frame.
For example, if resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_b, then
r_rel = resolve2(frame_b.R, frame_b.r_0 - frame_a.r0); v_rel = der(r_rel);
is returned (r_rel = resolve2(frame_b.R, frame_b.r_0 - frame_a.r0)), i.e., the derivative of the relative distance from frame_a to frame_b, resolved in frame_b. If resolveInFrameAfterDifferentiation = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.world, then v_rel is additionally transformed to:
v_rel = resolve1(frame_b.R, der(r_rel))
The cut-force and the cut-torque in frame_resolve are always zero, whether frame_resolve is connected or not.
If get_angles = true, the 3 angles to rotate frame_a into frame_b along the axes defined by parameter sequence are returned. For example, if sequence = {3,1,2} then frame_a is rotated around angles[1] along the z-axis, afterwards it is rotated around angles[2] along the x-axis, and finally it is rotated around angles[3] along the y-axis and is then identical to frame_b. The 3 angles are returned in the range
-π <= angles[i] <= π
There are two solutions for "angles[1]" in this range. Via parameter guessAngle1 (default = 0) the returned solution is selected such that |angles[1] - guessAngle1| is minimal. The relative transformation matrix between frame_a and frame_b may be in a singular configuration with respect to "sequence", i.e., there is an infinite number of angle values leading to the same relative transformation matrix. In this case, the returned solution is selected by setting angles[1] = guessAngle1. Then angles[2] and angles[3] can be uniquely determined in the above range.
The parameter sequence has the restriction that only values 1,2,3 can be used and that sequence[1] ≠ sequence[2] and sequence[2] ≠ sequence[3]. Often used values are:
sequence = {1,2,3} // Cardan or Tait-Bryan angle sequence
= {3,1,3} // Euler angle sequence
= {3,2,1}
Extends from Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.Internal.PartialRelativeSensor (Base class for relative sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| animation | = true, if animation shall be enabled (show arrow) |
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which vectors are resolved before differentiation (world, frame_a, frame_b, or frame_resolve) |
| get_r_rel | = true, to measure the relative position vector from the origin of frame_a to frame_b |
| get_v_rel | = true, to measure the relative velocity of the origin of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
| get_a_rel | = true, to measure the relative acceleration of the origin of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
| get_w_rel | = true, to measure the relative angular velocity of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
| get_z_rel | = true, to measure the relative angular acceleration of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
| 3 angles to rotate frame_a into frame_b along the axes defined in "sequence" | |
| get_angles | = true, to measure the 3 rotation angles |
| sequence | If get_angles=true: Angles are returned to rotate frame_a around axes sequence[1], sequence[2] and finally sequence[3] into frame_b |
| guessAngle1 | If get_angles=true: Select angles[1] such that abs(angles[1] - guessAngle1) is a minimum [rad] |
| Animation | |
| if animation = true | |
| arrowColor | Color of relative arrow from frame_a to frame_b |
| specularCoefficient | Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) |
| Advanced | |
| if get_v_rel or get_a_rel or get_z_rel | |
| resolveInFrameAfterDifferentiation | Frame in which vectors are resolved after differentiation (world, frame_a, frame_b, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| frame_resolve | If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the output signals are resolved in this frame |
| r_rel[3] | Relative position vector frame_b.r_0 - frame_a.r_0 resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [m] |
| v_rel[3] | Relative velocity vector [m/s] |
| a_rel[3] | Relative acceleration vector [m/s2] |
| angles[3] | Angles to rotate frame_a into frame_b via 'sequence' [rad] |
| w_rel[3] | Relative angular velocity vector [1/s] |
| z_rel[3] | Relative angular acceleration vector [1/s2] |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsolutePosition
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsolutePositionMeasure absolute position vector of the origin of a frame connector
The absolute position vector of the origin of frame_a is determined and provided at the output signal connector r.
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the position vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and r is resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_a, the output vector is computed as:
r = MultiBody.Frames.resolve2(frame_a.R, frame_b.r_0);
Extends from Internal.PartialAbsoluteSensor (Base class for absolute sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector r shall be resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a of which the absolute kinematic quantities are measured |
| r[3] | Absolute position vector resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [m] |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which output vector r is optionally resolved |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteVelocity
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteVelocityMeasure absolute velocity vector of origin of frame connector
The absolute velocity vector of the origin of frame_a is determined and provided at the output signal connector v.
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the velocity vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and v is resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_a, the output vector is computed as:
v0 = der(frame_a.r_0); v = MultiBody.Frames.resolve2(frame_a.R, v0);
Extends from Internal.PartialAbsoluteSensor (Base class for absolute sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector v shall be resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a of which the absolute kinematic quantities are measured |
| v[3] | Absolute velocity vector resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [m/s] |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which output vector v is optionally resolved |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteAngles
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteAnglesMeasure absolute angles between frame connector and the world frame
This model determines the 3 angles to rotate the world frame into frame_a along the axes defined by parameter sequence. For example, if sequence = {3,1,2} then the world frame is rotated around angles[1] along the z-axis, afterwards it is rotated around angles[2] along the x-axis, and finally it is rotated around angles[3] along the y-axis and is then identical to frame_a. The 3 angles are returned in the range
-π <= angles[i] <= π
There are two solutions for "angles[1]" in this range. Via parameter guessAngle1 (default = 0) the returned solution is selected such that |angles[1] - guessAngle1| is minimal. The transformation matrix between the world frame and frame_a may be in a singular configuration with respect to "sequence", i.e., there is an infinite number of angle values leading to the same relative transformation matrix. In this case, the returned solution is selected by setting angles[1] = guessAngle1. Then angles[2] and angles[3] can be uniquely determined in the above range.
The parameter sequence has the restriction that only values 1,2,3 can be used and that sequence[1] ≠ sequence[2] and sequence[2] ≠ sequence[3]. Often used values are:
sequence = {1,2,3} // Cardan or Tait-Bryan angle sequence
= {3,1,3} // Euler angle sequence
= {3,2,1}
Extends from Internal.PartialAbsoluteSensor (Base class for absolute sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sequence | Angles are returned to rotate world frame around axes sequence[1], sequence[2] and finally sequence[3] into frame_a |
| guessAngle1 | Select angles[1] such that abs(angles[1] - guessAngle1) is a minimum [rad] |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a of which the absolute kinematic quantities are measured |
| angles[3] | Angles to rotate world frame into frame_a via 'sequence' [rad] |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteAngularVelocity
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.AbsoluteAngularVelocityMeasure absolute angular velocity of frame connector
The absolute angular velocity of frame_a with respect to the world frame is determined and provided at the output signal connector w.
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the angular velocity is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and w is resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_a, the output vector is computed as:
w = MultiBody.Frames.angularVelocity2(frame_a.R);
Extends from Internal.PartialAbsoluteSensor (Base class for absolute sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector w shall be resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a of which the absolute kinematic quantities are measured |
| w[3] | Absolute angular velocity vector of frame_a with respect to world frame, resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [rad/s] |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which w is optionally resolved |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativePosition
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativePositionMeasure relative position vector between the origins of two frame connectors
The relative position vector between the origins of frame_a and frame_b are determined and provided at the output signal connector r_rel.
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the position vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_b | Resolve vector in frame_b |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and r_rel is resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_a, the output vector is computed as:
r_rel = MultiBody.Frames.resolve2(frame_a.R, frame_b.r_0 - frame_a.r_0);
Extends from Internal.PartialRelativeSensor (Base class for relative sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector r_rel shall be resolved (world, frame_a, frame_b, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| r_rel[3] | Relative position vector resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which r_rel is optionally resolved |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeVelocity
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeVelocityMeasure relative velocity vector between the origins of two frame connectors
The relative velocity vector between the origins of frame_a and of frame_b are determined and provided at the output signal connector v_rel. This vector is defined as:
r_rel = MultiBody.Frames.resolve2(frame_a.R, frame_b.r_0 - frame_a.r_0); v_rel = der(r_rel);
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the velocity vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_b | Resolve vector in frame_b |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and v_rel is resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_b, the output vector is computed as:
r_rel = MultiBody.Frames.resolve2(frame_a.R, frame_b.r_0 - frame_a.r_0); v_rel_a = der(r_rel); v_rel = MultiBody.Frames.resolveRelative(frame_a.R, frame_b.R, v_rel_a);
Extends from Internal.PartialRelativeSensor (Base class for relative sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector v_rel shall be resolved (world, frame_a, frame_b, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| v_rel[3] | Relative velocity vector resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [m/s] |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which v_rel is optionally resolved |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeAngles
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeAnglesMeasure relative angles between two frame connectors
This model determines the 3 angles to rotate frame_a into frame_b along the axes defined by parameter sequence. For example, if sequence = {3,1,2} then frame_a is rotated around angles[1] along the z-axis, afterwards it is rotated around angles[2] along the x-axis, and finally it is rotated around angles[3] along the y-axis and is then identical to frame_b. The 3 angles are returned in the range
-π <= angles[i] <= π
There are two solutions for "angles[1]" in this range. Via parameter guessAngle1 (default = 0) the returned solution is selected such that |angles[1] - guessAngle1| is minimal. The relative transformation matrix between frame_a and frame_b may be in a singular configuration with respect to "sequence", i.e., there is an infinite number of angle values leading to the same relative transformation matrix. In this case, the returned solution is selected by setting angles[1] = guessAngle1. Then angles[2] and angles[3] can be uniquely determined in the above range.
The parameter sequence has the restriction that only values 1,2,3 can be used and that sequence[1] ≠ sequence[2] and sequence[2] ≠ sequence[3]. Often used values are:
sequence = {1,2,3} // Cardan or Tait-Bryan angle sequence
= {3,1,3} // Euler angle sequence
= {3,2,1}
Extends from Internal.PartialRelativeSensor (Base class for relative sensor models), Modelica.Icons.RoundSensor (Icon representing a round measurement device).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sequence | Angles are returned to rotate frame_a around axes sequence[1], sequence[2] and finally sequence[3] into frame_b |
| guessAngle1 | Select angles[1] such that abs(angles[1] - guessAngle1) is a minimum [rad] |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| angles[3] | Angles to rotate frame_a into frame_b via 'sequence' [rad] |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeAngularVelocity
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.RelativeAngularVelocityMeasure relative angular velocity between two frame connectors
The relative angular velocity between frame_a and frame_b is determined and provided at the output signal connector w_rel.
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the angular velocity is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_b | Resolve vector in frame_b |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
In this basic sensor model, the connector frame_resolve is always enabled. If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the vector w_rel is resolved in the frame to which frame_resolve is connected.
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_a, the output vector is computed as:
// Relative orientation object from frame_a to frame_b R_rel = MultiBody.Frames.relativeRotation(frame_a.R, frame_b.R); // Angular velocity resolved in frame_a w_rel = MultiBody.Frames.angularVelocity1(R_rel);
Extends from Internal.PartialRelativeSensor (Base class for relative sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector w_rel shall be resolved (world, frame_a, frame_b, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| w_rel[3] | Relative angular velocity vector between frame_a and frame_b resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [rad/s] |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which w_rel is optionally resolved |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.Distance
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.DistanceMeasure the distance between the origins of two frame connectors
The distance between the origins of frame_a and of frame_b are determined and provided at the output signal connector distance. This distance is always positive. Derivatives of this signal can be easily obtained by connecting the block Modelica.Blocks.Continuous.Der to "distance" (this block performs analytic differentiation of the input signal using the der(…) operator).
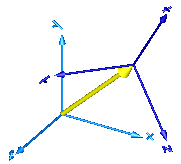
In the following figure the animation of a Distance sensor is shown. The light blue coordinate system is frame_a, the dark blue coordinate system is frame_b, and the yellow arrow is the animated sensor.
If the distance is smaller as parameter s_small (in the "advanced" menu), it is approximated such that its derivative is finite for zero distance. Without such an approximation, the derivative would be infinite and a division by zero would occur. The approximation is performed in the following way: If distance > s_small, it is computed as sqrt(r*r) where r is the position vector from the origin of frame_a to the origin of frame_b. If the distance becomes smaller as s_small, the "sqrt()" function is approximated by a second order polynomial, such that the function value and its first derivative are identical for sqrt() and the polynomial at s_small. Furthermore, the polynomial passes through zero. The effect is, that the distance function is continuous and differentiable everywhere. The derivative at zero distance is 3/(2*s_small).
Extends from Interfaces.PartialTwoFrames (Base model for components providing two frame connectors + outer world + assert to guarantee that the component is connected), Modelica.Icons.RectangularSensor (Icon representing a linear measurement device).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| animation | = true, if animation shall be enabled (show arrow) |
| if animation = true | |
| arrowColor | Color of relative arrow from frame_a to frame_b |
| specularCoefficient | Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) |
| Advanced | |
| s_small | Prevent zero-division if distance between frame_a and frame_b is zero [m] |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a fixed to the component with one cut-force and cut-torque |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b fixed to the component with one cut-force and cut-torque |
| distance | Distance between the origin of frame_a and the origin of frame_b |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.CutForce
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.CutForceMeasure cut force vector
The cut-force acting between the two frames to which this model is connected, is determined and provided at the output signal connector force (= frame_a.f). If parameter positiveSign = false, the negative cut-force is provided (= frame_b.f).
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the force vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and output force is resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
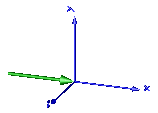
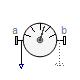
In the following figure the animation of a CutForce sensor is shown. The dark blue coordinate system is frame_b, and the green arrow is the cut force acting at frame_b and with negative sign at frame_a.
Extends from Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.Internal.PartialCutForceSensor (Base class to measure cut force and/or torque between two frames, defined by components).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| animation | = true, if animation shall be enabled (show arrow) |
| positiveSign | = true, if force with positive sign is returned (= frame_a.f), otherwise with negative sign (= frame_b.f) |
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector(s) is/are resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| if animation = true | |
| forceColor | Color of force arrow |
| specularCoefficient | Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| force[3] | Cut force resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [N] |
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| frame_resolve | Output vectors are optionally resolved in this frame (cut-force/-torque are set to zero) |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.CutTorque
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.CutTorqueMeasure cut torque vector
The cut-torque acting between the two frames to which this model is connected, is determined and provided at the output signal connector torque (= frame_a.t). If parameter positiveSign = false, the negative cut-torque is provided (= frame_b.t).
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the torque vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and output torque is resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
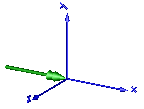
In the following figure the animation of a CutTorque sensor is shown. The dark blue coordinate system is frame_b, and the green arrow is the cut torque acting at frame_b and with negative sign at frame_a.
Extends from Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.Internal.PartialCutForceSensor (Base class to measure cut force and/or torque between two frames, defined by components).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| animation | = true, if animation shall be enabled (show arrow) |
| positiveSign | = true, if torque with positive sign is returned (= frame_a.t), otherwise with negative sign (= frame_b.t) |
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector(s) is/are resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| if animation = true | |
| torqueColor | Color of torque arrow |
| specularCoefficient | Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| torque[3] | Cut torque resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame |
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| frame_resolve | Output vectors are optionally resolved in this frame (cut-force/-torque are set to zero) |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.CutForceAndTorque
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.CutForceAndTorqueMeasure cut force and cut torque vector
The cut-force and cut-torque acting between the two frames to which this model is connected, are determined and provided at the output signal connectors force (= frame_a.f) and torque (= frame_a.t). If parameter positiveSign = false, the negative cut-force and cut-torque is provided (= frame_b.f, frame_b.t).
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which frame the two vectors are resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vector in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vector in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vector in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameAB.frame_resolve, the conditional connector "frame_resolve" is enabled and the output vectors force and torque are resolved in the frame, to which frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it must be connected.
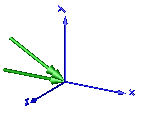
In the following figure the animation of a CutForceAndTorque sensor is shown. The dark blue coordinate system is frame_b, and the green arrows are the cut force and the cut torque, respectively, acting at frame_b and with negative sign at frame_a.
Extends from Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.Internal.PartialCutForceSensor (Base class to measure cut force and/or torque between two frames, defined by components).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| animation | = true, if animation shall be enabled (show force and torque arrow) |
| positiveSign | = true, if force and torque with positive sign is returned (= frame_a.f/.t), otherwise with negative sign (= frame_b.f/.t) |
| resolveInFrame | Frame in which output vector(s) is/are resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| if animation = true | |
| forceColor | Color of force arrow |
| torqueColor | Color of torque arrow |
| specularCoefficient | Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| force[3] | Cut force resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame [N] |
| torque[3] | Cut torque resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame |
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| frame_resolve | Output vectors are optionally resolved in this frame (cut-force/-torque are set to zero) |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.Power
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.PowerMeasure power flowing from frame_a to frame_b
This component provides the power flowing from frame_a to frame_b as output signal power.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.RoundSensor (Icon representing a round measurement device), Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Interfaces.PartialTwoFrames (Base model for components providing two frame connectors + outer world + assert to guarantee that the component is connected).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a fixed to the component with one cut-force and cut-torque |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b fixed to the component with one cut-force and cut-torque |
| power | Power at frame_a as output signal [W] |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.TransformAbsoluteVector
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.TransformAbsoluteVectorTransform absolute vector in to another frame
The input vector "Real r_in[3]" is assumed to be an absolute kinematic quantity of frame_a that is defined to be resolved in the frame defined with parameter "frame_r_in". This model resolves vector r_in in the coordinate system defined with parameter "frame_r_out" and returns the transformed output vector as "Real r_out[3]";
Extends from Modelica.Icons.RoundSensor (Icon representing a round measurement device).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_r_in | Frame in which vector r_in is resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| frame_r_out | Frame in which vector r_in shall be resolved and provided as r_out (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system from which absolute kinematic quantities are measured |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which r_in or r_out is optionally resolved |
| r_in[3] | Input vector resolved in frame defined by frame_r_in |
| r_out[3] | Input vector r_in resolved in frame defined by frame_r_out |
 Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.TransformRelativeVector
Modelica.Mechanics.MultiBody.Sensors.TransformRelativeVectorTransform relative vector in to another frame
The input vector "Real r_in[3]" is assumed to be a relative kinematic quantity between frame_a and frame_b that is defined to be resolved in the frame defined with parameter "frame_r_in". This model resolves vector r_in in the coordinate system defined with parameter "frame_r_out" and returns the transformed output vector as "Real r_out[3]";
Extends from Internal.PartialRelativeSensor (Base class for relative sensor models).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_r_in | Frame in which vector r_in is resolved (world, frame_a, frame_b, or frame_resolve) |
| frame_r_out | Frame in which vector r_in shall be resolved and provided as r_out (world, frame_a, frame_b, or frame_resolve) |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| frame_a | Coordinate system a |
| frame_b | Coordinate system b |
| frame_resolve | Coordinate system in which r_in or r_out is optionally resolved |
| r_in[3] | Input vector resolved in frame defined by frame_r_in |
| r_out[3] | Input vector r_in resolved in frame defined by frame_r_out |